Hva er galle og gallestein?
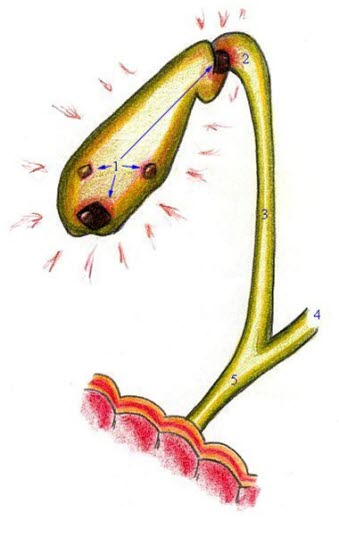 Galleblære - med stein
Galleblære - med steinI leveren dannes en væske vi kaller galle. Denne oppbevares i galleblæren til tarmen har bruk for den etter et måltid. Via gallegangene føres gallen ut i tarmen hvor den tømmer seg i tolvfingertarmen (duodenum). Gallen består av vann, kolesterol, fettstoffer, gallesalter og bilirubin. Gallesaltene er viktige for fordøyelsen da de bryter ned fettet i maten. Bilirubin er fargestoffet som gir avføringen sin brune farge. Hvis det er for mye kolesterol, gallesalter eller bilirubin i gallesaften kan den krystallisere og forme stein inne i galleblæra. 90% av gallesteiner er kolesterolsteiner.
Steiner i galleblæra kan passere ut av galleblæra og over i gallegangen. Steiner i gallegangen kan kile seg fast og blokkere for utslipp fra galleblæra og leveren. Ved tilstopping av gallegangen vil det etter hvert oppstå gulsott (gulfarging av huden som er lettest å se på hvitøyet), avføringen blir lys og urinen mørk. Gulsott er imidlertid en uvanlig komplikasjon til akutt betennelse i galleblæren.
Vil du vite mer
Dette dokumentet er basert på det profesjonelle dokumentet Kolecystitt, akutt . Referanselisten for dette dokumentet vises nedenfor
- Strasberg SM. Acute calculous cholecystitis. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 2804-11. PubMed
- Gurusamy KS, Davidson C, Gluud C, Davidson BR. Early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for people with acute cholecystitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 6. Art. No.: CD005440. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005440.pub3. DOI
- Stinton LM, Shaffer EA. Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer. Gut Liver 2012;6:172-187 PubMed
- Trowbridge RL, Rutkowski NK, Shojania KG. Does this patient have acute cholecystitis? JAMA 2003;289:80-6. Journal of the American Medical Association
- Indar AA, Beckingham IJ. Acute cholecystitis. BMJ 2002;325:639-643. British Medical Journal
- Jain A, Mehta N, Secko M, et al. Jain A et al. History, physical exam. Laboratory testing and emergency department ultrasonography for the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis. Acad Emerg Med 2016 . doi:10.1111/acem.13132 DOI
- Singer AJ, McCracken G, Henry MC, et al.Correlation among clinical, laboratory, and hepatobiliary scanning findings in patients with suspected acute cholecystitis. Ann Emerg Med 1996;28:267-272. PubMed
- Kiewiet JJ, Leeuwenburgh MM, Bipat S, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic performance of imaging in acute cholecystitis. Radiology 2012; 264: 708-20. Radiology
- Chatziioannou SN, Moore WH, Ford PV, Dhekne RD. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy is superior to abdominal ultrasonography in suspected acute cholecystitis. Surgery 2000; 127: 609-13. Surgery
- Haug JB (red). Kolecystitt og kolangitt. Nasjonal faglig retningslinje for bruk av antibiotika i sykehus. Helsedirektoratet 2013.
- Gutt CN, et al. Acute cholecystitis: Early versus delayed cholecystectomy, a multicenter randomized trial. Ann Surg 2013; 258: 385. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a1599b DOI
- Cao AM, Eslick GD, Cox MR. Early laparoscopic cholecystectomy is superior to delayed acute cholecystitis: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Surg Endosc. 2016 Mar;30(3):1172-82. pmid: 26139487. PubMed
- Gurusamy KS, Rossi M, Davidson BR. Percutaneous cholecystostomy for high-risk surgical patients with acute calculous cholecystitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013 Aug 12;8:CD007088. PMID: 23939652. PubMed
- Lund H, Bisgaard T, Schulze S, Rosenberg K, Kristiansen VB. Behandlingen af akut cholecystitis i Danmark. Ugeskr Læger 2003; 165: 4221-3. PubMed
- Siddiqui T, MacDonald A, Chong PS, Jenkins JT. Early versus delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am J Surg 2008; 195: 40-7. PubMed
- Brazzelli M, Cruickshank M, Kilonzo M, et al. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cholecystectomy compared with observation/conservative management for preventing recurrent symptoms and complications in adults presenting with uncomplicated symptomatic gallstones or cholecystitis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2014 ;18(55):1-101, v-vi. doi: 10.3310/hta18550. DOI